JWT Authentication
Kusk allows you to protect your APIs in Kubernetes using JWT. In this guide you'll learn how to add JWT authentication to your API.
For the purposes of this example, we're using Auth0's JWT authentication.
Example
1. Create an Auth0 JWT authentication
Signup for an account at Auth0.
Create an Auth0 API Application. Go to Applications > APIs
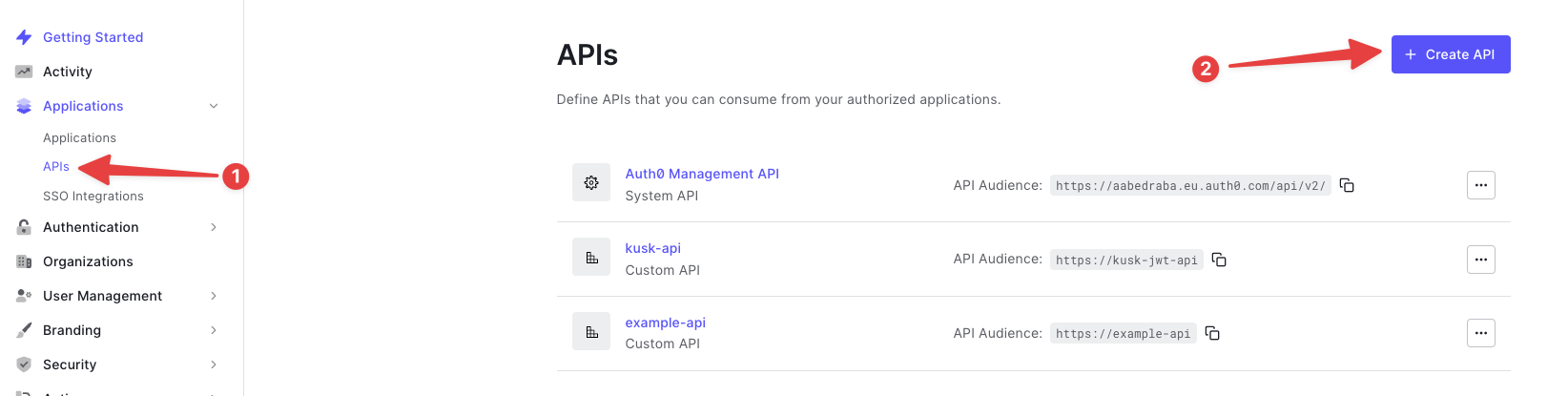
Configure the following Auth0 Application fields:
- Name (e.g.
example-api) - Identifier (e.g.
https://example-api) - Signing algorithm: RS256
- Name (e.g.
Take note of your Auth0 domain, which you can find here:
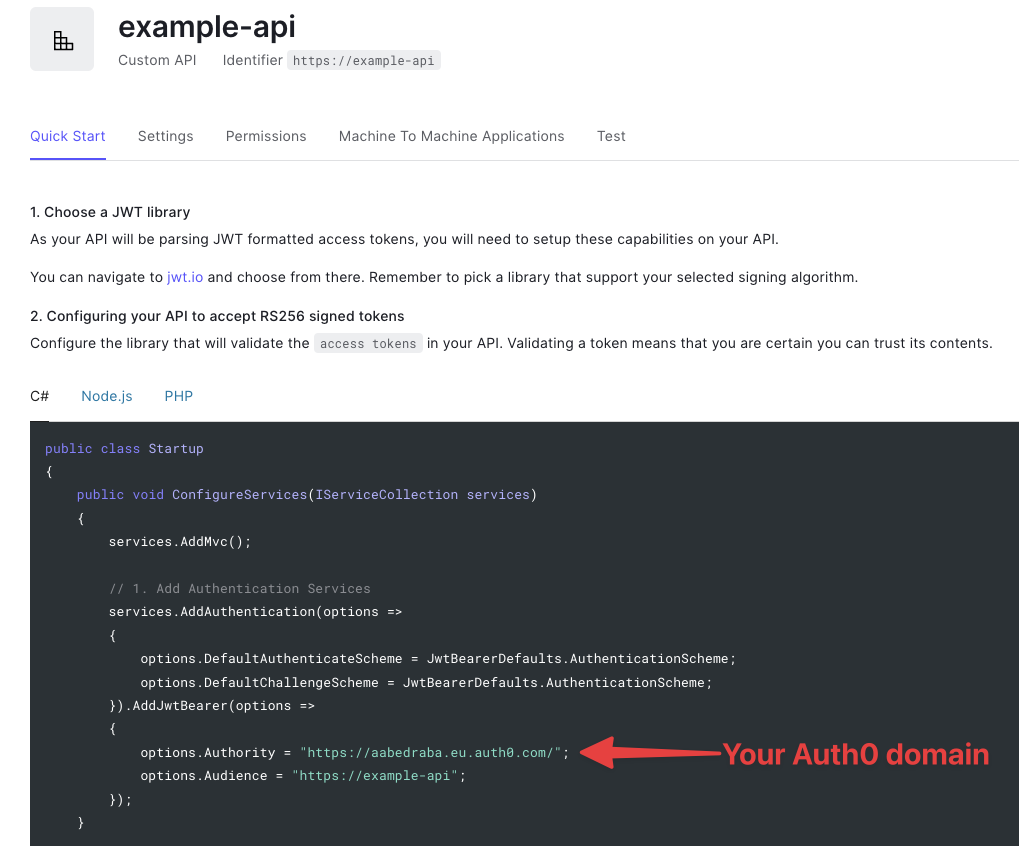
2. Deploy an API application to your Kubernetes cluster
kubectl create deployment hello-world --image=kubeshop/kusk-hello-world:v1.0.0
kubectl expose deployment hello-world --name hello-world-svc --port=8080
deployment.apps/hello-world created
service/hello-world-svc exposed
3. Create the OpenAPI definition to expose your API using Kusk
A minimal example of the configuration for the JWT filter is:
openapi: 3.1.0
info:
title: jwt-oauth0
description: jwt-oauth0
version: 0.1.0
x-kusk:
upstream:
service:
name: hello-world-svc
namespace: default
port: 8080
auth:
jwt:
providers:
- name: kusk-gateway-jwt
issuer: $ISSUER_URL
audiences:
- $JWT_AUDIENCE
jwks: $JWKS_URL
paths:
/hello:
get:
description: Returns a hello world greeting
operationId: /hello
responses: {}
You are required to change:
issuer(for example:https://$AUTH0_DOMAIN)audiences(for example:https://$AUTH0_IDENTIFIER, you can get the Identifier field from the Settings tab)jwks(for example:https://$AUTH0_DOMAIN/.well-known/jwks.json)
After that, deploy the API by running:
kusk deploy -i api.yaml
4. Get a token from Auth0
The best way to get a token to test authentication with from Auth0 is using the curl command they offer in the test tab:
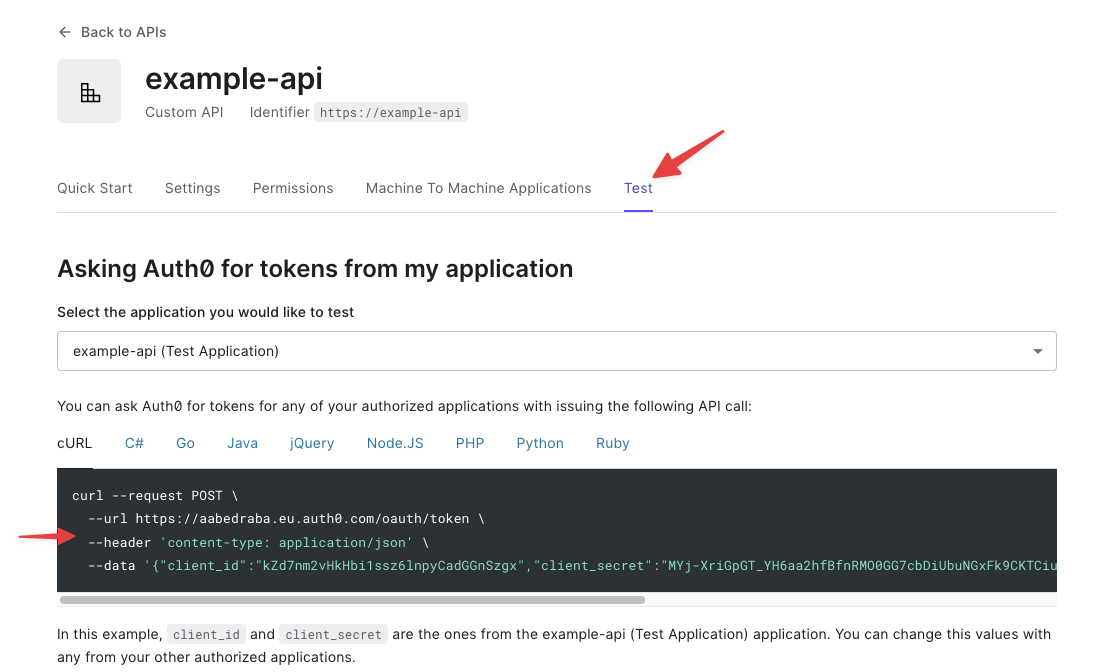
Run the curl command and take note of the token:
curl --request POST \
--url https://aabedraba.eu.auth0.com/oauth/token \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '{"client_id":"$CLIENT_ID","client_secret":"$CLIENT_SECRET","audience":"https://example-api","grant_type":"client_credentials"}'
{"access_token":"TOKEN_TO_COPY","expires_in":86400,"token_type":"Bearer"}
5. Test your authenticated API
Get the IP address of Kusk by running:
kusk ip
> 12.34.56.78
curl -H 'Authorization: Bearer "YOUR_TOKEN"' 12.34.56.78/hello
{
"message": "Hello from an implemented service!"
}
Example without Bearer token specified
curl 12.34.56.78/hello
> Jwt is missing
Example with invalid Bearer token
curl -H 'Authorization: Bearer invalid-token' 12.34.56.78/hello
> Jwt header is an invalid JSONShould pass since Bearer token is present
Your API is now authenticated!
With Kusk, authenticating your APIs using JWT tokens is as easy as adding an extension to your OpenAPI definition. Stay safe out there!