OAuth2 via OIDC
OAuth2 ensures that your web application (upstream) doesn't get requests which are not authenticated and authorized. It effectively helps to protect your web application.
This is for web applications authentication. If you want to secure your APIs you can use JWT authentication
Kusk implements the OpenID Connect (OIDC) layer which ensures you can choose any OAuth2 provider and Kusk will support it as long as the OAuth2 provider also supports OIDC.
Kusk makes it easy to configure OAuth2, using the auth option in you StaticRoute.
The OAuth2 feature is currently under active development. See upstream issues.
Setup Guide
We'll go through step-by-step of configuring OAuth2. In this example we'll be using Auth0 as OAuth2 provider.
1. Configuring Auth0
- Signup for an account at Auth0.
- Create an Auth0 Application
- Configure the following Auth0 Application fields: (KUSK_IP is the IP of the Kusk's LoadBalancer, you can obtain it by running
1. Allowed Callback URLs (e.g. `http://**KUSK_IP**/oauth2/callback`)
2. Allowed Logout URLs (e.g. `http://**KUSK_IP**/oauth2/signout`)kusk ip) - Take note of the credentials as we will need this later on:
{
"client_id": "go8brZmF6eE6r7TObzpGaD5KFjJkm6Qb",
"client_secret": "bkryzZGGA6Ko0VGnUEl_1YeREMHDpjGP8r1BTN1HYlmXpAWaiWNkD4bqIDuAuCKV"
}
2. Deploy your web application to Kusk
Deploy your web application to Kubernetes or use our example application:
kubectl create deployment oauth-app --image=kubeshop/kusk-oauth-app-example:v1.0.0
kubectl expose deployment oauth-app --name oauth-app-svc --port=3000
deployment.apps/oauth-app created
service/oauth-app-svc exposed
3. Expose the web-application with OAuth using Kusk
The example below ensures the whole API is protected via OAuth2, and that the upstream oauth-app-svc can be only accessed when authenticated and authorized.
apiVersion: gateway.kusk.io/v1alpha1
kind: StaticRoute
metadata:
name: oauth-app-sample
spec:
fleet:
name: kusk-gateway-envoy-fleet
namespace: kusk-system
upstream:
service:
name: oauth-app-svc
namespace: default
port: 3000
auth:
oauth2:
token_endpoint: https://**YOUR_DOMAIN**.eu.auth0.com/oauth/token
authorization_endpoint: https://**YOUR_DOMAIN**.eu.auth0.com/authorize
credentials:
client_id: **CLIENTID**
client_secret: **CLIENT_SECRET**
redirect_uri: /oauth2/callback
redirect_path_matcher: /oauth2/callback
signout_path: /oauth2/signout
forward_bearer_token: true
auth_scopes:
- openid
You are required to change:
token_endpoint.authorization_endpoint.credentials.client_id.credentials.client_secret.auth_scopes: Strictly speaking this is not required but we strongly suggest enteringopenidfor testing purposes
After that, expose the web-application with Kusk by running:
kubectl apply -f static-route.yaml
4. Update EnvoyFleet ConfigMap
We need to include to client_secret to Envoy's ConfigMap, by running
kubectl edit -n kusk-system configmaps kusk-gateway-envoy-fleet
And then update the field inline_string replacing it with the client_secret obtained from Auth0.
secrets:
- name: token
generic_secret:
secret:
inline_string: "<stub_token_secret>" # <- replace with "CLIENT_SECRET"
Finally, you should save the configuration and the changes will be applied.
5. Restart Envoy Fleet
As we currently have upstream issues with Envoy waiting to be fixed, the temporal solution is to restart Envoy manually (this only needs to be done once):
For this:
- Port-Forward into Envoy's control plane:
kubectl port-forward --namespace kusk-system deployment/kusk-gateway-envoy-fleet 19000:19000
- Restart Envoy by making a POST request to
/quitquitquit
curl -X POST 'http://localhost:19000/quitquitquit'
- Wait until the changes to be propogated, this could take a while. To know if the Envoy has restarted, check if the Envoy container has restarted
kubectl get pods -w -n kusk-system --selector=app.kubernetes.io/instance=kusk-gateway-envoy-fleet
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kusk-gateway-envoy-fleet-6f9ff68bcd-jxlwk 1/1 Running 1 (30s ago) 1h6. Test using the browser
You're all set now, test your OAuth2 implementation through the browser by visiting Kusk's LoadBalancer. Get the URL with:
kusk ip
100.12.34.56
Now visit the address in the browser and you'll see that you web application is now using Auth0's OAuth page:
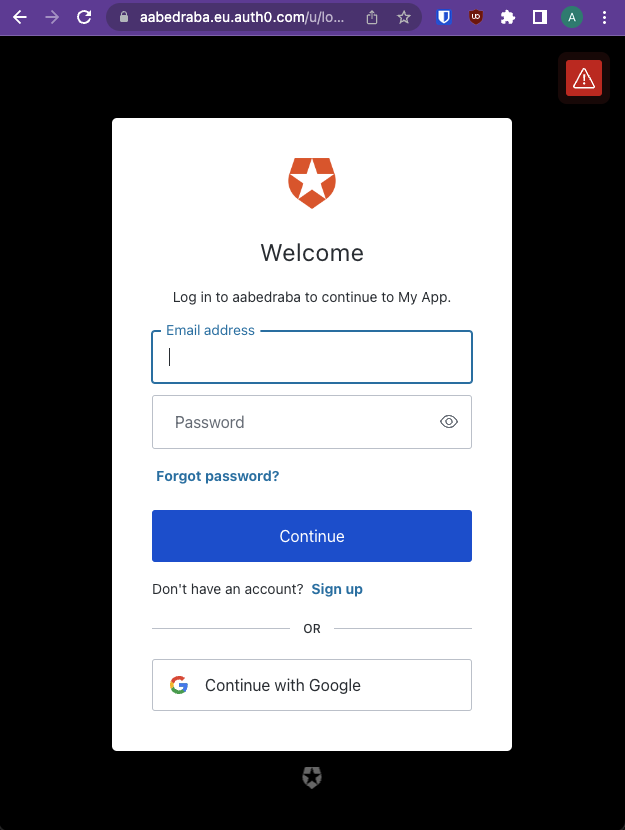
Upstream Issues
Certain OAuth2 features are blocked/constrained by upstream issues. Please see:
- Segmentation Fault after `assert failure: false. Details: attempted to add shared target SdsApi <NAME_OF_SECRET> to initialized init manager Server.
SecretDiscoveryServiceServer:StreamSecretsissues.
So the implementation is constrained by these issues, which should be fixed by January 2023.